Note: This post contains 11 photos with captions and a little narrative. Photos by me (Bruce) taken with a SONY alpha 6400 or Google Pixel 6 Pro unless otherwise indicated. (Photos by Linda taken with a Google Pixel 6.)
SATURDAY 28 October 2023 — NTNP 11 of 14 — West Florida Boundary and Vicksburg Civil War sites

Heading south on the Natchez Trace NP from our Boondockers Welcome site, our first stop was the West Florida Boundary parking area. It was also a trailhead for a section of the Natchez Trace. This photo provides a sense of scale to the trail and surrounding forest.
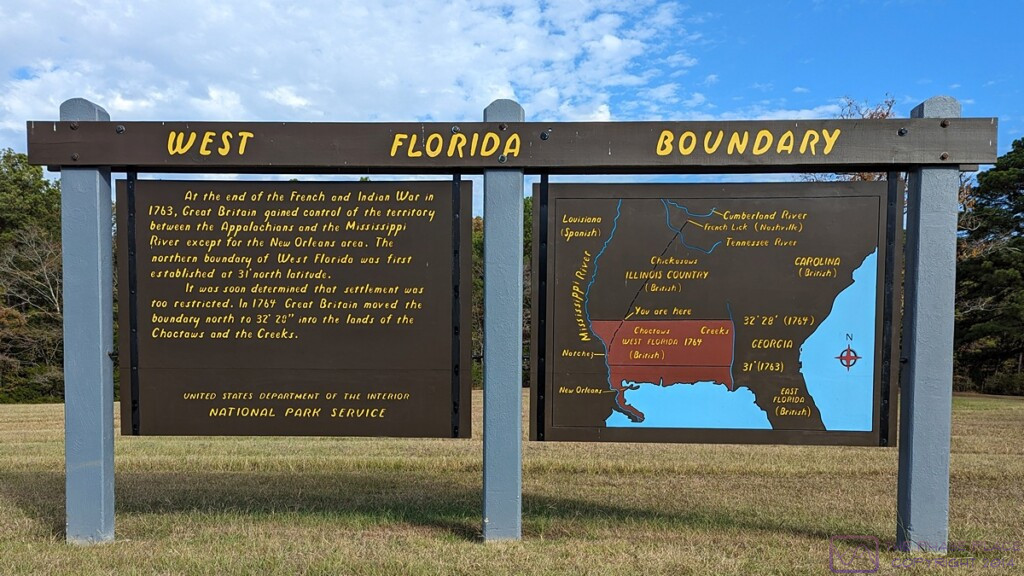
WEST FLORIDA BOUNDARY sign. This image file is 1200×675 pixels and can be viewed a full-resolution on a suitable device. The sign on the right with the map shows the territory known as “West Florida.” The lower lower/narrow strip along the sea was the extent of the territory as of the end of the French and Indian War in 1763, at which time Great Britain gained control of the lands west to the Mississippi River. The northern boundary of this area was set at 31 deg N latitude. The region was quickly considered too restricted for settlement, and a year later (1764) the British (unilaterally) moved the northern boundary to 32 deg 28 min N latitude into the lands of the Choctaws and Creeks, approximately tripling its size.

This photo was taken at the Reservoir Overlook for the Ross R. Barnett Reservoir just on the NTNP near Ridgeland, Mississippi. Our BW location was a bit northeast of here, closer to Canton, Mississippi. The reservoir is on the Pearl River. The photo is a composite of five images taken with the SONY alpha 6400. It is 1200×327 pixels and can be viewed at full-resolution on a suitable device by clicking on the photo.

Another composite image from the Reservoir Overlook, this one taken with a Google Pixel 6. (Photo by Linda)

The RESERVOIR OVERLOOK information sign. The Ross R. Barnett Reservoir is formed by a large earthen dame and covers 50 square miles. It is administered by the Pearl River Valley Water Supply District, an agency of the State of Mississippi.
Although our focus for this trip was the Natchez Trace National Parkway, we realized that we were close enough to Vicksburg, Mississippi that we decided to detour over there and have a look. One of the major tourist destinations in the Vicksburg area is the Vicksburg National Military Park and the Vicksburg National Battlefield. Once we were there, we discovered the USS Cairo Gunboat and Museum site within the NMP, and checked it out. The museum was not open when we visited the site, but we found the ship, as shown in the following four photographs, fascinating.
Paraphrased from Wikipedia: The USS Cairo was the lead ship of the City-class casemate ironclads built at the beginning of the American Civil War to serve as river gunboats for the Union. Cairo is named for Cairo, Illinois. In June 1862, she captured the Confederate garrison of Fort Pillow on the Mississippi, enabling Union forces to occupy Memphis. As part of the Yazoo Pass Expedition, she was sunk in the Yazoo River (a spur of the Mississippi River) on 12 December 1862 (near Vicksburg), while clearing mines for the attack on Haines Bluff. Cairo was the first ship ever to be sunk by a mine remotely detonated by hand. The remains of the Cairo can be viewed at Vicksburg National Military Park with a museum of its weapons and naval stores.
The remains of the ship were discovered in 1956 and salvaged in 1964-65. It was listed in the National Register of Historic Places on 3 September 1971. By 1980 Congress had authorized the National Park Service to accept the boat, move it to the Vicksburg NMP, and put in on display in conjunction with a museum to house the recovered artifacts and tell the story of the boat and its role in the Civil War.

This photo has nothing to do with the Civil War. I’ve outlined the fuel economy readout on our F-150 instrumentation cluster. Folks, you can’t make this stuff up; it really does say 29.1 (miles per gallon). We had recently filled up the fuel tank and only traveled 39.3 miles, as shown in the lower left, so this was obviously light travel and slightly downhill. Although this MPG is not sustainable under normal driving conditions, the number in the upper right indicates that we could travel another 747 miles before running out of fuel if we could maintain this MPG.
…